Blog
Electrical motors are machines designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. While they are available in numerous variations, they can be categorized into two main classifications: AC motors and DC motors.
Both AC motors and DC motors have the same function; that is, to convert electrical energy to mechanical energy. However, when choosing a motor for an application, it is important to know the difference between AC and DC motors as each has distinct construction, powering, and controlling requirements. The following article discusses the differences between the two motor types, including key design and operating characteristics, advantages, and applications.
An Overview of AC Motors
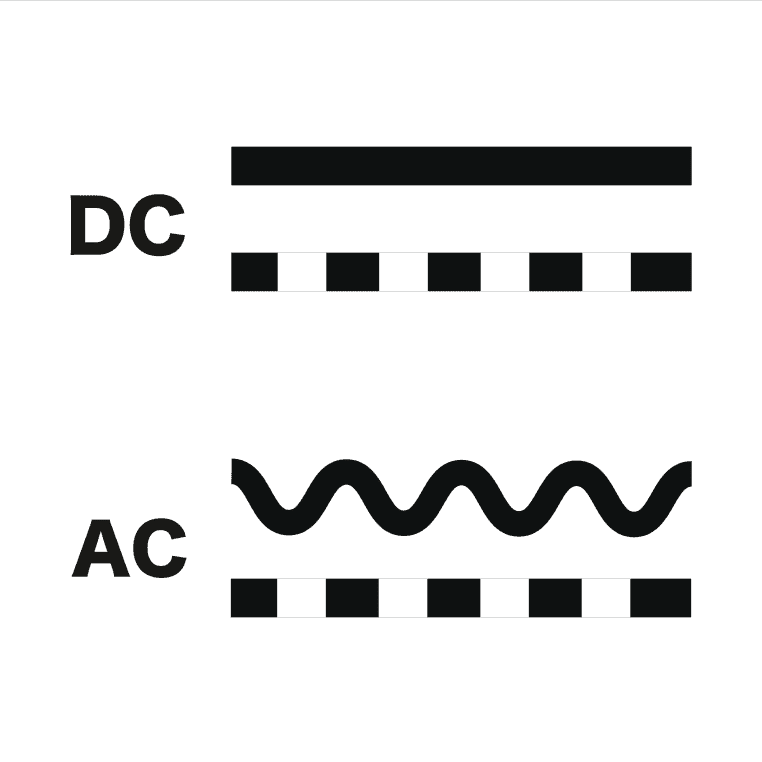
As suggested by the name, AC motors rely on alternating current (AC) to generate mechanical energy. The standard design consists of a stator with winding imbedded around the circumference and a freely rotating metal part (i.e., the rotor) at the center.
When current is applied to the stator windings in an AC motor, a rotating magnetic field is generated. This magnetic field induces an electrical current within the electrically conductive rotor and, consequently, forms a second rotating magnetic field. The interaction between the first magnetic field and second magnetic field causes the rotor and, as the magnetic field alternates between coil pairs, the motor to turn.
Two of the critical factors to keep in mind when choosing an AC motor for an application are:
- Running speed (in revolutions per minute): the maximum speed a motor can achieve calculated by the following formula: (120 x AC power frequency in Hz) ÷ poles of the motor
- Starting torque: the amount of torque a motor generates when starting at zero speed
An Overview of DC Motors
DC motors rely on direct current (DC) with constant voltage to generate mechanical energy. DC motors consist of a rotating armature winding (i.e., the rotor) and a field stator with windings that form a set of stationary electromagnets. The other key component of a DC motor is the commutator which is attached to the armature.
As current flows through a DC motor, a magnetic field is generated within the field stator and around the armature winding. The interaction between these two magnetic fields produces an electromagnetic force which causes the armature to rotate. The commutator changes the direction of current flow into the armature and thereby allowing it to continue spinning as long as current flows through the system.
DC motors can be used to produce different levels of speed and torque. Adjusting the voltage levels applied to the armature or the static field current changes the output speed.
Advantages of AC Motors vs. DC Motors
Both AC motors and DC motors demonstrate unique advantages that make them suitable for different applications. Below we outline the benefits offered by both types of motors.
Advantages of AC motors include:
- Lower startup power demands
- Better control over starting current levels and acceleration
- Broader customizability for different configuration requirements and changing speed and torque requirements
- Greater durability and longevity
Advantages of DC motors include:
- Simpler installation and maintenance requirements
- Higher startup power and torque
- Faster response times for start/stop and acceleration
- Wider variety for different voltage requirements
Applications of AC Motors vs. DC Motors
As indicated above, AC motors and DC motors are suited for different applications. In the industrial sector, the durability, flexibility, and efficiency of AC motors make them ideal for use in applications for a wide range of devices, including appliances, compressors, computers, conveyors, fans and other HVAC equipment, pumps, and transportation equipment. The faster response times and more stable torque and speed levels offered by DC motors make them well-suited for use in fabrication and production equipment, elevators, vacuums, and material handling equipment.
Contact the Electric Motor Experts at Renown Electric Today
Both AC motors and DC motors play a critical role in power generation operations across a wide range of industrial, commercial, and residential applications. As both motor types offer advantages and disadvantages, it is important to understand the difference between them to ensure you pick the right one for your facility. If you need assistance choosing an AC motor or a DC motor suitable for your needs, turn to the experts at Renown Electric.
At Renown Electric, we specialize in the repair and service of electric motors. Equipped with nearly 40 years of experience working with motors, we have the knowledge and skills to repair, remanufacture, or replace motors for nearly any application.
Contact Us today to find out more about which motor is right for your facility.






1 Comment
Francky
Thank you for sharing this informative article on Electric Motors