Infrared Thermography Functions
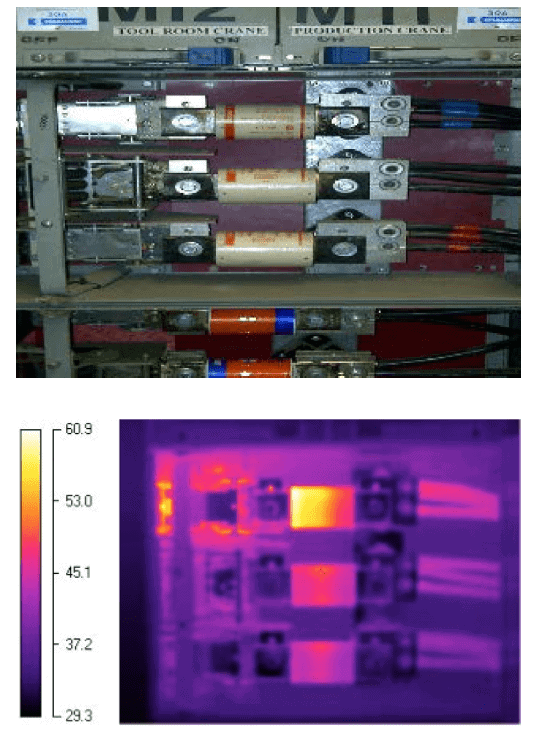
Different objects emit varying levels of infrared radiation—i.e., heat. By employing infrared thermography, operators can detect these normally invisible radiation levels and create a visual representation of the heat distribution. The infrared thermography technology allows system operators and technicians to verify normal operation or locate abnormal heat patterns and other anomalies within machines and systems. The advantage of this technology is that it provides users with the capacity to detect system issues and correct them before they cause extensive system damage or production shutdowns.
While operating infrared imaging technology is relatively simple, interpreting the visual information collected by the systems is more complex and challenging. With proper training and experience, asset managers and maintenance personnel can utilize the data provided by infrared cameras to make improvements to the system maintenance, monitor system performance, and enhance production quality.
When using infrared thermography on mechanical equipment (such as motors and rotating equipment), certain conditions are required. Operators—referred to as thermographers—must have a solid understanding of basic radiometry and heat transfer principles, familiarity with the equipment’s operational parameters, and substantial knowledge of the capabilities and limitations of infrared cameras. Most of these inspections focus on comparing the overall thermal patterns to establish the health of the overall system, rather than emphasizing absolute temperature measurements.
Why Thermal Imaging?
There are several methods of monitoring the electrical and mechanical conditions of a motor. However, thermal imaging proves to be the most efficient and fastest screening tool available. Infrared thermography allows for the detection of abnormal thermal signatures, which might relate to any number of conditions that produce high levels of heat, such as:
- Excessive friction
- Increased electrical resistance
- Decreased cooling fluid levels or airflow
- Issues relating to current flow
After detecting abnormal thermal signatures, operators can employ additional inspection methods, such as vibration, airborne ultrasonic, or motor circuit analysis, to pinpoint the precise cause of the thermal anomaly.
Detecting Issues Proactively with Infrared Thermography
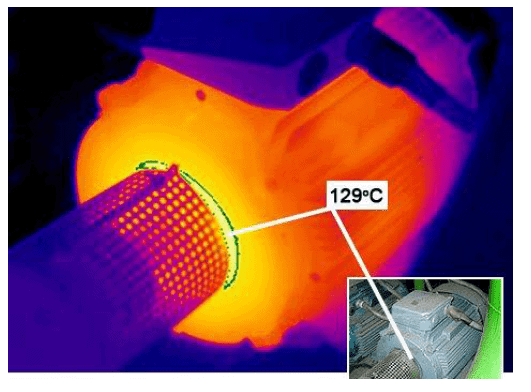
Unexpected system damage and failure significantly impact the productivity of a facility by imposing production shutdowns, as well increases the costs of operation, maintenance, and total equipment investment. Preventing these issues requires predictive maintenance procedures, such as employing infrared thermography, to proactively detect potential system issues. Some of the applications where thermal imaging accomplishes this objective include:
- Bearing inspection. The rise in the surface temperature of a bearing, detected through a change in its thermal signature, might point to abnormal friction from under or over lubrication, poor maintenance or a bad bearing.
- Low speed equipment inspection. Employing infrared thermography facilitates the inspection of low speed equipment, including overhead conveyors or idlers.
- High temperature refractory insulation monitoring. Thermal imaging allows operators to monitor the condition of internal motor components such as refractory insulation, as well as calculate the remaining refractory thickness.
Planned Maintenance vs Costly Downtime
The use of infrared thermography to inspect equipment and systems allows facilities to conduct planned maintenance outages aimed towards repairing potential issues before they lead to more critical, expensive, and unplanned system failures.
Although inspecting mechanical systems with infrared thermography presents some challenges, the overall financial and professional advantages make the technology worth the investment. Personnel operating thermal imaging equipment must have both an adequate understanding of how the piece of mechanical equipment functions and fundamental knowledge of heat transfer theory to interpret the thermal data provided by the imaging technology. Used along with other applicable predictive maintenance methods, infrared thermography can provide facilities with a comprehensive understanding of the health of their systems.
Aspects & Defects of Commutator Skins
Our technical guide discusses some of the most frequent commutator defects, their causes and how to recognize them, as well as specific information on erosion, pitted skin, bar markings, abnormal wear and patchiness.
Download Your CopyInfrared Thermography Solutions
Rely on us to use thermal imaging as a part of our custom preventive and predictive maintenance program to diagnose and resolve problems before they lead to costly system failures.
Contact Us


