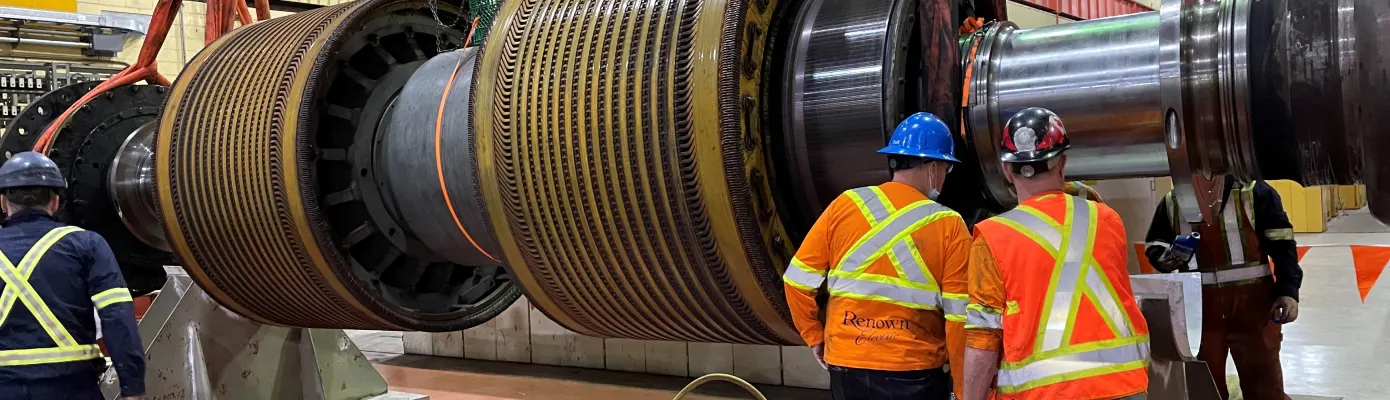
Modern elevator motors, whether powered by a variable frequency drive (VFD) for AC motors or a DC controller, are highly efficient, but the control systems generate significant electrical noise. This noise manifests as high-frequency current spikes, also known as common mode currents, which can cause damage to the motor bearings. Renown Electric Motors and Repair conducted two case studies to evaluate the effectiveness of CoolBLUE inductive absorbers and NaLA noise line absorbers in mitigating this issue. The goal was to reduce common mode currents and prevent bearing damage, thereby extending the life of the elevator motors.
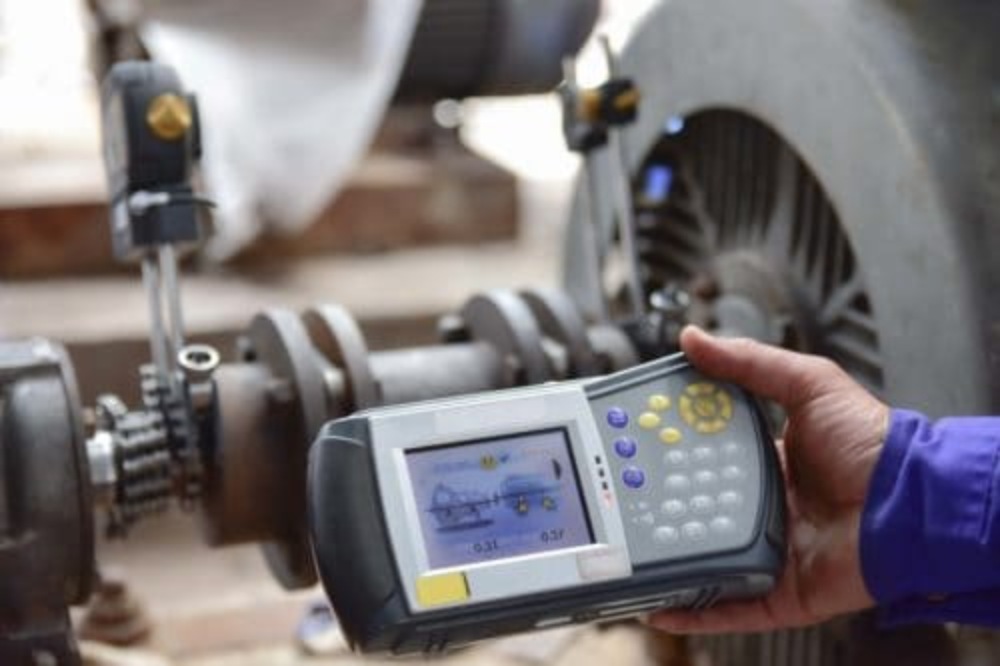

Equipment
Rogowski Coil, Bull Gearless Hoist Motor, CoolBLUE
Inductive Absorbers and NaLA Noise Line Absorbers
Objective
Determine if CoolBLUE and NaLA absorbers could effectively reduce the high-frequency common mode currents produced by VFDs and DC controllers
Project Duration
Testing conducted before and after the installation of the CoolBLUE and NaLA absorbers
Challenge
The main challenge was the pervasive electrical noise generated by the motor control systems. This noise, which can be measured as voltage spikes or common mode current, was causing accelerated wear and damage to the motor bearings. Standard solutions like ferrite chokes were found to be insufficient, highlighting the need for a more effective solution.
The Plan – DC Motors
To test our theory, we used a Rogowski coil, a toroidal coil specifically tuned to measure high frequency current pulses that are superimposed on the control signal, on the output of a DC controller. This drive was connected to a Bull Gearless DC hoist motor in a busy Commercial Retail and Office Complex in downtown Toronto. The motor and drive are separated by approximately 20 feet of inverter duty cable.
The Plan – AC Motors
We installed a Rogowski Coil (used to measure Alternating Current (A/C) and high speed current pulses) on the output of the VFD on an overhead geared traction machine with a 40HP AC Hoist motor to measure the actual electrical noise level caused by the switching of the IGBT’s.
The Conclusion
After conducting tests of CoolBLUE inductive absorbers and NaLA noise line absorbers, Renown found that the absorbers perform very effectively to reduce common mode currents (“voltage spikes”) well within safe operating limits of the bearings.
We recommend optimizing the number and type of absorbers depending on the particular motor with which they are to be installed, and expect common mode current reductions in the area of 65%. The absorbers will effectively eliminate the damage that leads to harmful vibrations, extending the life of your motor bearings and reducing incidents of maintenance.
To learn more about CoolBLUE inductive absorbers and NaLA noise line absorbers, download our CoolBLUE Design and Installation Guides today.
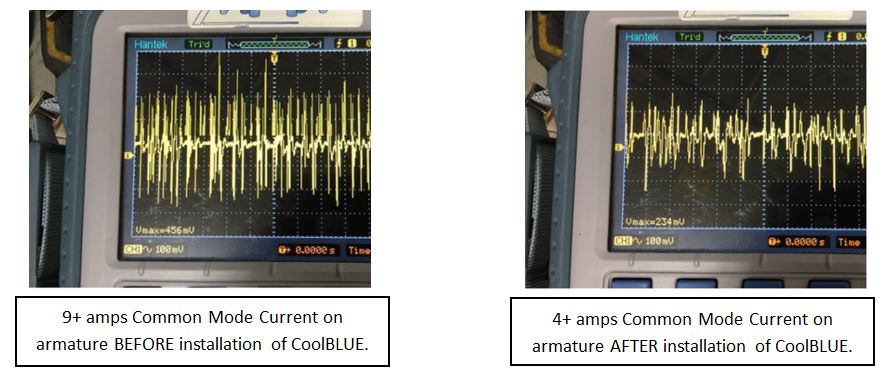
DC Hoist Motor Common Mode Current – Before & After CoolBLUE installation:
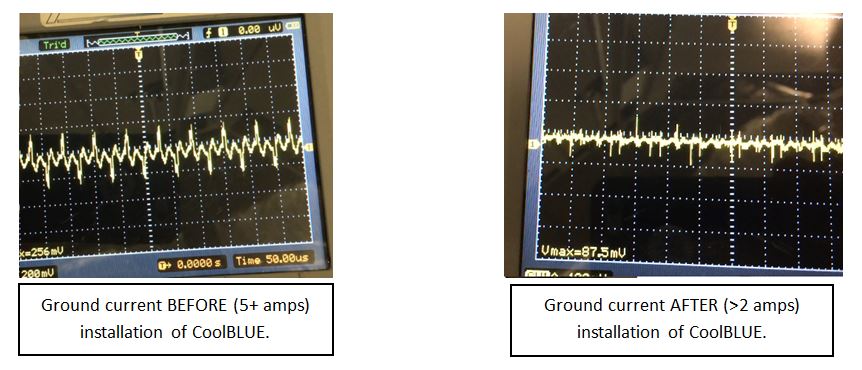
AC Motor Ground Current – Before & After CoolBLUE installation:
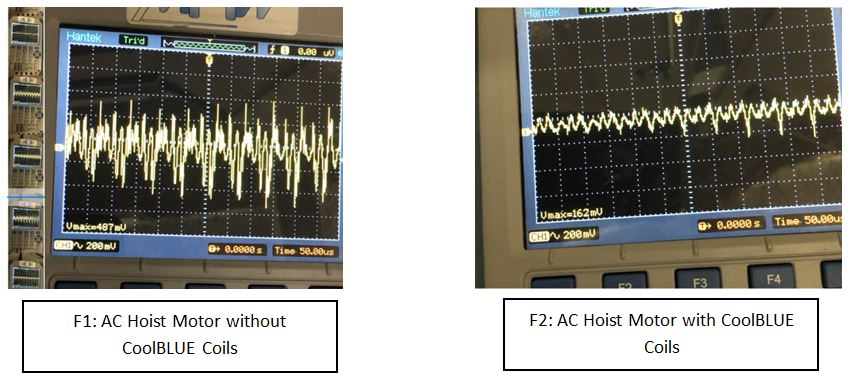
AC Hoist Motor Electrical Noise – Before & After CoolBLUE installation:
Process
The project followed a clear, three-phase process for both the AC and DC motor tests.
Baseline Measurement: A Rogowski coil, a specialized toroidal coil for measuring high-frequency currents, was connected to an oscilloscope. Measurements of the common mode current were taken at the output of the motor’s control system (VFD or DC controller) before any mitigation devices were installed. This established a baseline for the electrical noise present in the system.
Equipment Installation: CoolBLUE inductive absorbers and NaLA noise line absorbers were installed onto the output of the drives. These devices were strategically placed to absorb and dissipate the high-frequency common mode currents.
Post-Installation Analysis: A second set of measurements was taken using the same Rogowski coil and oscilloscope setup to quantify the reduction in common mode current. The results from this phase were then compared to the baseline measurements to determine the effectiveness of the absorbers.

Get in Touch with our Skilled Team
No matter your industry or application, we’re here for you. Contact us to learn more about our extensive capabilities, and how we serve clients across industries to ensure their motors are operating at their best.